Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
DSS example#
Find the linear combinations of multichannel data that maximize repeatability over trials.
Uses meegkit.dss0().
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from meegkit import dss
from meegkit.utils import fold, rms, tscov, unfold
rng = np.random.default_rng(5)
Create simulated data#
# Data are time * channel * trials.
n_samples = 100 * 3
n_chans = 30
n_trials = 100
noise_dim = 20 # dimensionality of noise
# Source signal
source = np.hstack((
np.zeros((n_samples // 3,)),
np.sin(2 * np.pi * np.arange(n_samples // 3) / (n_samples / 3)).T,
np.zeros((n_samples // 3,))))[np.newaxis].T
s = source * rng.standard_normal((1, n_chans)) # 300 * 30
s = s[:, :, np.newaxis]
s = np.tile(s, (1, 1, 100))
# Noise
noise = np.dot(
unfold(rng.standard_normal((n_samples, noise_dim, n_trials))),
rng.standard_normal((noise_dim, n_chans)))
noise = fold(noise, n_samples)
# Mix signal and noise
SNR = 0.1
data = noise / rms(noise.flatten()) + SNR * s / rms(s.flatten())
Apply DSS to clean them#
# Compute original and biased covariance matrices
c0, _ = tscov(data)
# In this case the biased covariance is simply the covariance of the mean over
# trials
c1, _ = tscov(np.mean(data, 2))
# Apply DSS
[todss, _, pwr0, pwr1] = dss.dss0(c0, c1)
z = fold(np.dot(unfold(data), todss), epoch_size=n_samples)
# Find best components
best_comp = np.mean(z[:, 0, :], -1)
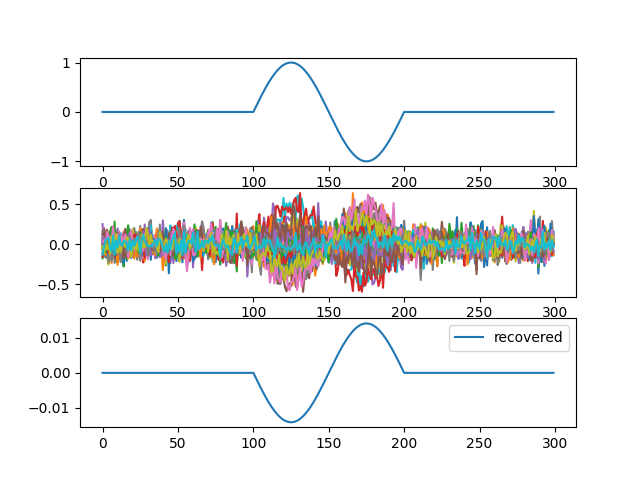
Plot results#
f, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(3, 1)
ax1.plot(source, label="source")
ax2.plot(np.mean(data, 2), label="data")
ax3.plot(best_comp, label="recovered")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.222 seconds)